May 23, 2024
By Nick Lorem
Exploring the Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Arthritis Relief
Arthritis is a broad term that refers to more than 100 different health conditions affecting the joints. The most common types include knee osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, each presenting differently but often leading to reduced mobility and discomfort.
Typical symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. These symptoms can fluctuate in severity and vary depending on which joints are affected and the specific type of arthritis present.
The causes of arthritis are complex. Genetics, previous injuries, autoimmune responses, and even lifestyle factors such as inactivity or obesity can all contribute. Understanding these causes is crucial in guiding treatment and pain management strategies.
For many people, arthritis pain goes beyond the physical. Living with chronic discomfort can impact sleep, mood, and everyday functioning, making managing joint pain not just a medical issue but a quality-of-life concern.
This article explores the benefits of shockwave therapy for arthritis. The treatment stimulates blood flow and activates natural healing responses in affected joints. By improving circulation and reducing inflammation, it may contribute to long-term pain reduction and better mobility.
Summary of the Content:
- Arthritis encompasses more than 100 conditions that cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, which can limit mobility and impact daily activities.
- Shockwave therapy is a noninvasive approach that uses pressure waves to enhance blood flow, stimulate nerves, and promote natural recovery in affected joints and soft tissues.
- The benefits of shockwave therapy for arthritis may include reducing pain, improving flexibility, and making activities like walking, standing, or climbing stairs easier.
- Biological effects include improved circulation, reduced inflammation, and tissue regeneration. These changes may support long-term joint health in arthritis and other musculoskeletal disorders.
- As a noninvasive option, shockwave therapy may be considered when medications or physiotherapy have not provided enough relief.
- Combining shockwave therapy with physiotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes may enhance results and reduce reliance on medications.
- Personalised plans created by healthcare professionals help align management strategies with each person’s conditions, goals, and lifestyle needs.
Understanding Shockwave Therapy
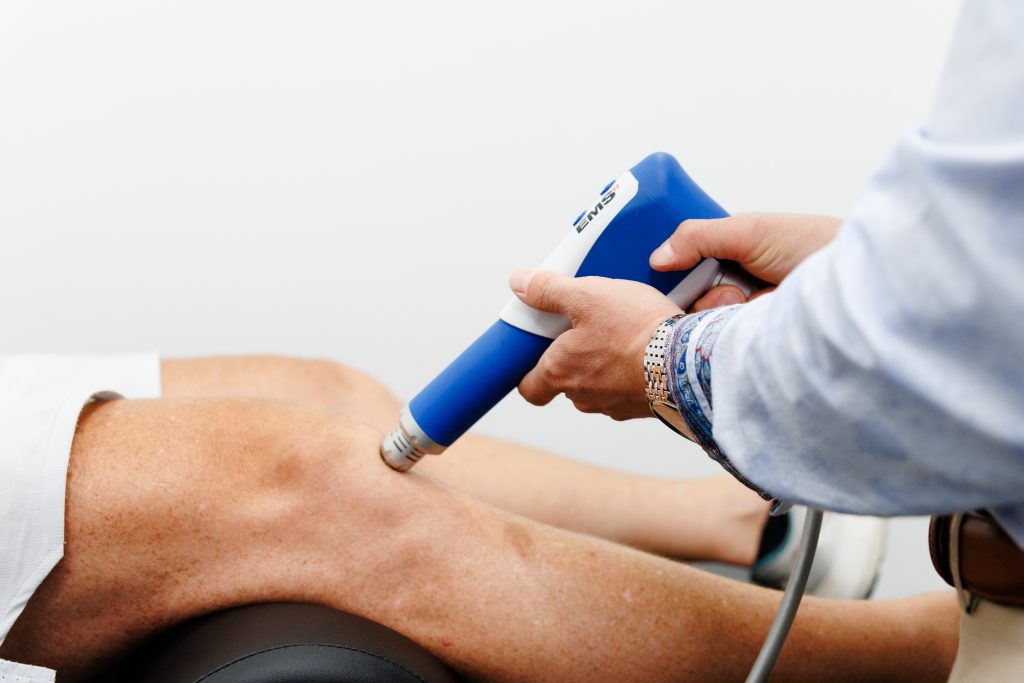
Shockwave therapy, also called extracorporeal shock wave therapy, is a noninvasive treatment. It uses a small handheld device to send strong sound waves into the body.
These sound waves are called pressure waves. They travel to the sore or stiff area to stimulate nerves, improve blood flow, and support healing in muscles and soft tissue.
This therapy doesn’t involve surgery, injections, or medication. Many people try it when traditional treatments like medicine or exercise aren’t giving enough pain relief.
Shockwave therapy offers a safe treatment with very few side effects. Some people may notice slight redness or tenderness in the affected area for a short time.
It has been approved for certain conditions, such as long-term tendon pain, in other countries, including the United States, by the FDA.
The following are the two main types of shockwave therapy:
- Radial shockwave therapy:
This type spreads energy over a wider area. It is often used for pain near the skin’s surface. - Focused shockwave therapy (focused ESWT):
This type sends energy deeper into the body. It is often used for more targeted or long-lasting pain in deeper joints or tissues.
Your therapist may use one or both types depending on your symptoms. They’ll also consider how you’ve responded to other treatments in the past.
Benefits and Effectiveness
Shockwave therapy is becoming a popular option for people with arthritis. Many people try it when other treatments have not worked well enough. This includes cases where medication, physical therapy, or rest have not provided lasting relief.
It’s also used to support the healing process, especially in joints and soft tissues. The goal is to help the body recover naturally with fewer side effects.
Reducing Pain and Improving Joint Function
Shockwave therapy can be particularly beneficial for individuals with knee arthritis, a common form of osteoarthritis. This condition often causes arthritis pain, stiffness, and reduced joint movement. Everyday tasks, such as walking, standing, or climbing stairs, can become difficult.
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy delivers sound waves to the joint to enhance blood flow, reduce inflammation and swelling, and alleviate discomfort.
It may offer several key benefits for those living with knee arthritis:
- It can help minimise pain that occurs during daily activities, such as walking, standing, or bending the knee.
- It may improve joint flexibility by increasing the range of motion of the knee, allowing it to bend or stretch further.
- It can make weight-bearing tasks, such as climbing stairs or standing for long periods, more manageable and comfortable.
- It may enhance outcomes when combined with physical therapy, helping people regain mobility more effectively.
- It has been shown to improve pain and function in people with knee osteoarthritis, according to a systematic review of clinical studies.
These improvements in movement and comfort may also support a more active lifestyle. Staying active can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce risk factors for joint damage.
Enhancing Healing Through Biological Mechanisms
Shockwave therapy not only helps with pain—it also works deep within the body to trigger natural healing processes at the cellular level.
These effects are especially beneficial in conditions such as arthritis and other musculoskeletal disorders, where damaged tissues require long-term support to recover and heal.
Some of the biological effects triggered by shockwave therapy include:
- It increases blood vessel formation (angiogenesis), which improves blood circulation and brings more oxygen and nutrients to damaged joints.
- It stimulates cell activity, encouraging the recovery of soft tissue structures, such as tendons, ligaments, and cartilage.
- It promotes tissue regeneration, allowing the body to gradually replace worn or damaged tissue with new, healthy tissue.
- It reduces long-term inflammation, which may lower the chance of further joint damage in chronic conditions.
- It activates cellular signalling pathways that help regulate pain and support healing — without relying on medication.
- It enhances metabolic activity in the affected area, supporting the healing process over several treatment sessions.
These effects are different from short-term pain relief. They contribute to deeper, biological recovery and can enhance the outcomes of physical medicine, movement therapy, and a healthy diet.
A Noninvasive Alternative to Surgical Options
For many people living with long-term arthritis pain, surgery may seem like the only option when other treatments haven’t helped enough.
Shockwave therapy offers a noninvasive alternative that doesn’t require hospitalisation, incisions, or extended recovery time.
The therapy delivers focused pressure waves through the skin without the need for injections, cuts, or surgical tools. It stimulates a response while keeping the surrounding tissues untouched.
Because it avoids surgical risks—like infection, anaesthesia, or lengthy downtime—it’s often considered a lower-risk option for some patients.
It may be especially useful when:
- Medications haven’t delivered lasting pain relief.
- Physiotherapy alone has not been effective.
- A person wants to delay or avoid joint replacement surgery.
Shockwave therapy can act as a middle-ground option between conservative care and surgery, giving patients more flexibility in how they approach their condition.
It may also reduce the need for more aggressive treatments and help people stick to a consistent care plan.
Working in Combination with Other Therapies
Shockwave therapy is often most effective when used as part of a wider treatment plan. It can be combined with physiotherapy, ultrasound therapy, and prescribed medication to create a balanced strategy for people living with arthritis.
This combined approach offers several advantages:
- It enables patients to manage pain more effectively by utilising multiple therapies that target various aspects of the condition.
- It can reduce reliance on medications alone, lowering the risks of side effects from long-term use.
- It encourages movement and function by combining the benefits of shockwave therapy with exercises prescribed by physiotherapists.
- It supports consistency in treatment, which is important for long-term success in pain management.
An integrated plan is not only about therapy and medication. Lifestyle adjustments, such as maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular low-impact exercise, also play a crucial role in managing arthritis pain.
Supporting Exercise and Physical Activity
Staying active is one of the most important parts of managing arthritis. Regular exercise helps keep joints flexible, strengthens muscles, and supports overall well-being.
For people living with arthritis pain, movement can sometimes feel difficult or discouraging. This is where shockwave therapy can play a supportive role. By helping to reduce pain, gentle movement can become more achievable, even for those with limited mobility.
Low-impact activities are often recommended for people with joint conditions because they are easier on the body while still providing benefits.
Examples include:
- Walking at a comfortable pace on flat surfaces can improve fitness without placing excessive stress on the joints.
- Swimming or other water-based exercise can make movement easier by reducing pressure on painful joints.
- Gentle stretching or yoga can help maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness in affected areas.
When paired with these types of activities, shockwave therapy can help individuals maintain consistency in their exercise routines. This makes it easier to complete daily tasks, such as carrying groceries, bending, or standing for extended periods of time.
Exercise also plays a role in promoting healing by improving circulation and joint health. Together with shockwave therapy, it may help improve pain levels over time and support long-term function.
Physical Medicine and Therapy
Physical therapy strengthens muscles and improves flexibility, which helps reduce stress on affected joints and surrounding soft tissues.
Occupational therapy also provides valuable support. It teaches practical strategies and introduces tools to make daily tasks easier, helping people maintain independence despite joint limitations.
Some examples of how these therapies assist in arthritis care include:
- Strengthening exercises can enhance joint stability. They also help reduce unnecessary strain.
- Stretching routines can increase flexibility. They may also ease stiffness in affected areas.
- Balance and coordination training can improve safety. They help lower the risk of falls.
- Adaptive aids provided by occupational therapists can help individuals maintain their independence and autonomy. These tools make tasks such as cooking, dressing, or writing more manageable.
When combined with shockwave therapy, physical therapy may deliver better outcomes. Shockwave therapy can reduce discomfort and promote healing. Therapy sessions then focus on building strength and function.
This combined approach may also lower the need for ongoing medication. It offers patients more balanced treatment options.
Both therapies are considered safe for many patients. However, people with certain health conditions should consult their healthcare provider. This helps avoid possible adverse events.
Managing Chronic Pain
Living with long-term pain can be overwhelming. For many patients, constant discomfort affects sleep, mood, work, and relationships, making life feel significantly worse.
Chronic pain is often linked to conditions such as arthritis, back injuries, and other musculoskeletal disorders. It may also develop as part of a broader disease process.
Managing this pain usually requires a plan that combines different approaches:
- Lifestyle adjustments, such as maintaining a healthy diet and staying active within safe limits, support general well-being.
- Targeted therapies, such as physiotherapy or guided movement programs, can help alleviate strain on the body.
- Medication may be prescribed, although doctors often try to limit long-term reliance on drugs alone.
Healthcare professionals design treatment plans tailored to each person’s specific condition, goals, and medical history. This approach helps make management strategies safe, realistic, and more effective over time.
Complementary approaches such as acupuncture or massage can also provide relief. These therapies support relaxation and comfort while reducing the need for invasive care.
Final Thoughts
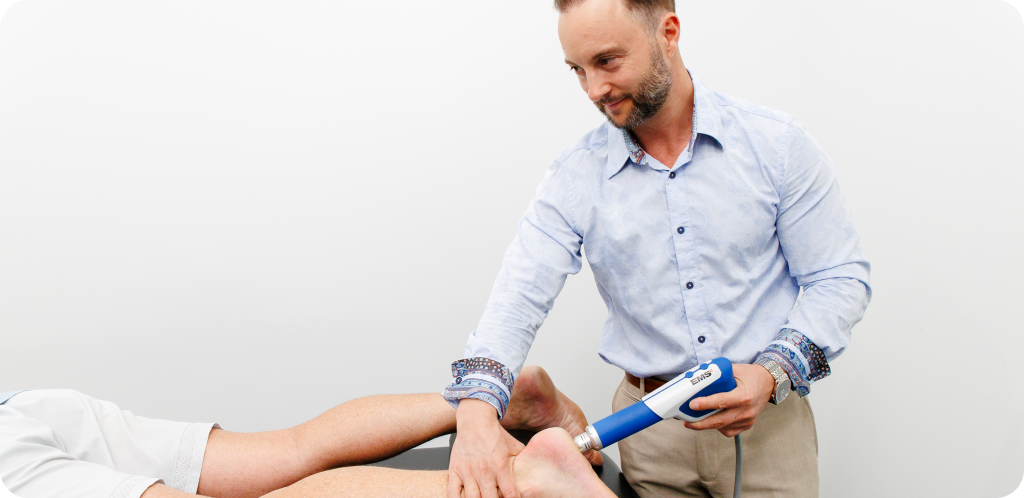
Shockwave therapy is a safe, noninvasive treatment that may help reduce arthritis-related pain and support better joint function. It offers patients another option for care.
The benefits of shockwave therapy for arthritis are often more effective when combined with physical therapy, appropriate medication, and lifestyle changes tailored to individual needs.
Current research supports its potential, but further studies are ongoing to understand how it can be used most effectively in different patient groups.
Every person’s condition is unique. That is why it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to create a personalised plan that meets your specific needs.
At Impact Shockwave and Technology Centre, our team is here to guide you through options and help determine if this therapy is right for you.
